Cypress NoBL CY7C1352G User Manual
Browse online or download User Manual for Unknown Cypress NoBL CY7C1352G. Cypress NoBL CY7C1352G User's Manual [pt]
- Page / 12
- Table of contents
- BOOKMARKS



Summary of Contents
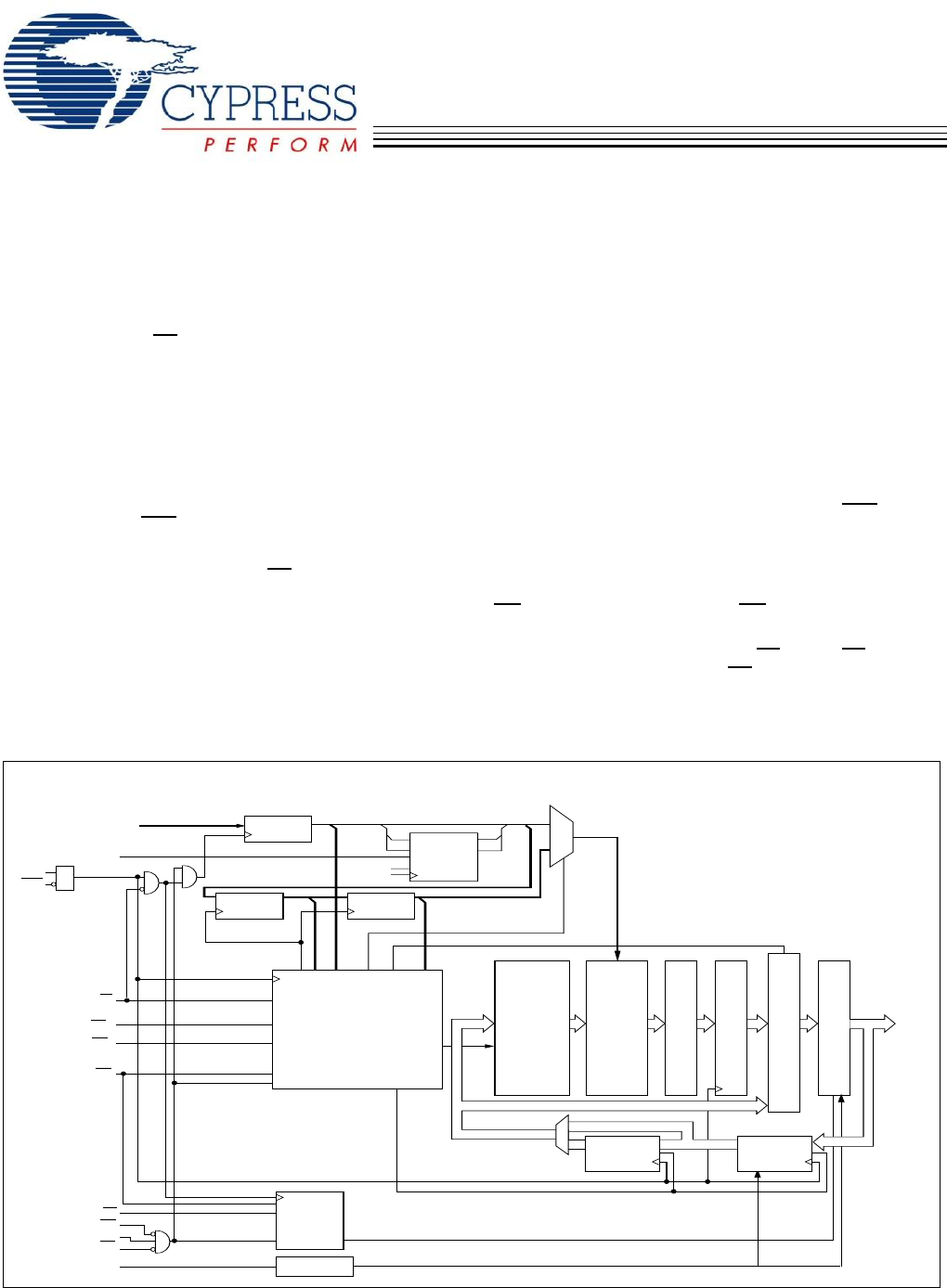
4-Mbit (256K x 18) Pipelined SRAM withNoBL™ ArchitectureCY7C1352GCypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 40
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 10 of 12NOP, STALL, and DESELECT Cycles[18, 19, 21]ZZ Mode Timing[22, 23]Notes: 21.The IGNORE CLOCK EDGE or
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 11 of 12© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006. The information contained herein is subject to change w
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 12 of 12Document History PageDocument Title: CY7C1352G 4-Mbit (256K x 18) Pipelined SRAM with NoBL™ Archite
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 2 of 12Selection Guide 250 MHz 200 MHz 166 MHz 133 MHz UnitMaximum Access Time 2.6 2.8 3.5 4.0 nsMaximum O
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 3 of 12Pin DefinitionsName I/O DescriptionA0, A1, A Input-SynchronousAddress Inputs used to select one of t
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 4 of 12Functional OverviewThe CY7C1352G is a synchronous-pipelined Burst SRAMdesigned specifically to elimi
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 5 of 12 Interleaved Burst Address Table (MODE = Floating or VDD)FirstAddressA1, A0SecondAddressA1, A0Third
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 6 of 12Maximum Ratings(Above which the useful life may be impaired. For user guide-lines, not tested.)Stora
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 7 of 12ISB4Automatic CEPower-down Current—TTL InputsVDD = Max, Device Deselected, VIN ≥ VIH or VIN ≤ VIL, f
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 8 of 12Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range[16, 17]Parameter Description–250 –200 –166 –133
CY7C1352GDocument #: 38-05514 Rev. *D Page 9 of 12Switching WaveformsRead/Write Timing[18, 19, 20]Notes: 18.For this waveform ZZ is tied low.19.When C
 (23 pages)
(23 pages)







Comments to this Manuals